Facing Earth's Sixth Mass Extinction: A Call to Protect Insects and Biodiversity
Our planet is experiencing its sixth mass extinction, primarily driven by human activities. Biodiversity is declining at unprecedented rates, with insects—vital to ecosystem health—suffering significant losses. A 2017 study reported a 76% decline in flying insect biomass over 27 years in German nature reserves (Hallmann et al., 2017). More recently, InsectChange noted an 80% drop in global insect biomass. These declines threaten essential ecosystem services, including pollination, nutrient cycling, and food production.
Why Insects Matter
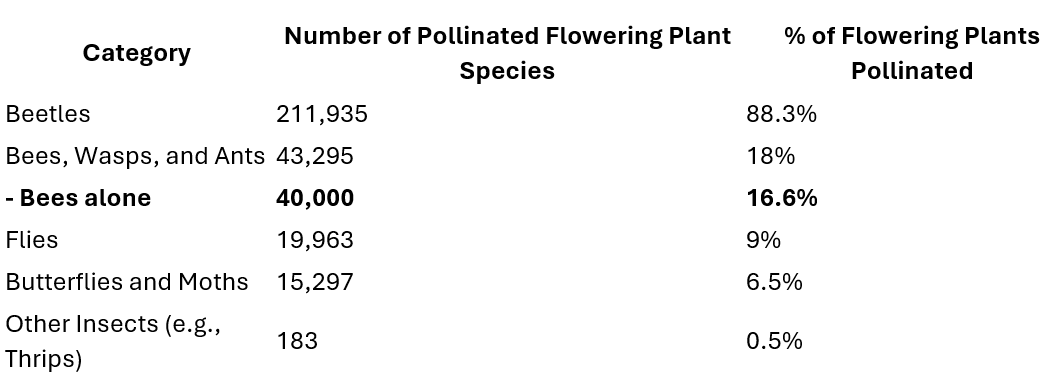
Insects are often celebrated for their role as pollinators, but there’s a common misconception that bees alone bear this responsibility. In reality, many insect species contribute to pollination, playing diverse and irreplaceable roles in ecosystems. Here’s a breakdown of pollinator contributions based on the Bugs: Our Backyard Heroes exhibition at the Museum of Victoria:
These figures highlight the diversity and importance of insect pollinators beyond bees. Beetles, often overlooked, are responsible for pollinating nearly half of all flowering plant species. While bees and wasps are vital contributors, the combined efforts of various insect categories ensure the stability of ecosystems and the production of fruits, vegetables, and other crops essential to human survival.
The Role of Native Plants in Supporting Insect Populations
Insects and native plants have co-evolved, forming interdependent relationships that are vital for ecological stability. Native plants provide specific resources—nectar, pollen, and shelter—that local insects need to survive. For example, milkweed species in North America support monarch butterflies by providing essential habitat and food for their larvae.
Incorporating native plants into private gardens can mitigate insect decline. Unlike exotic or ornamental species, native plants foster biodiversity and create vital refuges for insects. Even small-scale gardening efforts can bridge fragmented habitats and bolster local ecosystems.
MANA’s Initiatives in Biodiversity Conservation
At MANA, we are taking action to address the insect crisis. Our team is developing a comprehensive database linking native plants to their associated insect species, focusing on endangered varieties. This project aims to fill critical knowledge gaps in understanding these relationships.
MANA’s database will serve as a practical resource for gardeners, conservationists, and policymakers, guiding efforts to protect biodiversity. By promoting the cultivation of native plants, we hope to empower communities to make meaningful contributions to insect conservation.
What You Can Do
You can play a crucial role in safeguarding insect populations by taking simple yet impactful steps:
Plant Native Species: Choose plants indigenous to your region to provide food and habitat for local insects.
Reduce Pesticide Use: Avoid chemicals that harm insect populations and disrupt ecosystems.
Create Diverse Habitats: Incorporate elements like logs, rocks, and water sources into your garden to support a variety of species.
Stay Informed: Use tools like the YAFU app to learn more about sustainable products and their environmental impacts.
A Shared Responsibility
Saving insects and biodiversity isn’t just about preserving nature—it’s about ensuring a sustainable future for all life on Earth. Through individual actions and collective initiatives like MANA’s native plant database, we can address the biodiversity crisis together.
For updates on MANA’s native plant database and ways to get involved, visit [MANA’s website]. Every garden, every plant, and every effort counts. Let’s take action today for a thriving tomorrow.
References
Hallmann, C. A., et al. (2017). More than 75 percent decline over 27 years in total flying insect biomass in protected areas. PLOS ONE, 12(10), e0185809. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0185809
Gaume, L., & Desquilbet, M. (2024). InsectChange: Comment. Peer Community Journal. https://peercommunityjournal.org/item/10_24072_pcjournal_469/
EcoServants Project. (2023). The Importance of Native Plants: Supporting Local Biodiversity and Resilient Landscapes. https://ecoservantsproject.org/the-importance-of-native-plants-supporting-local-biodiversity-and-resilient-landscapes/
Audubon. (n.d.). Why Native Plants Matter. https://www.audubon.org/content/why-native-plants-matter
Bugs: Our Backyard Heroes. (2024). Museum of Victoria Exhibition. Melbourne, Australia